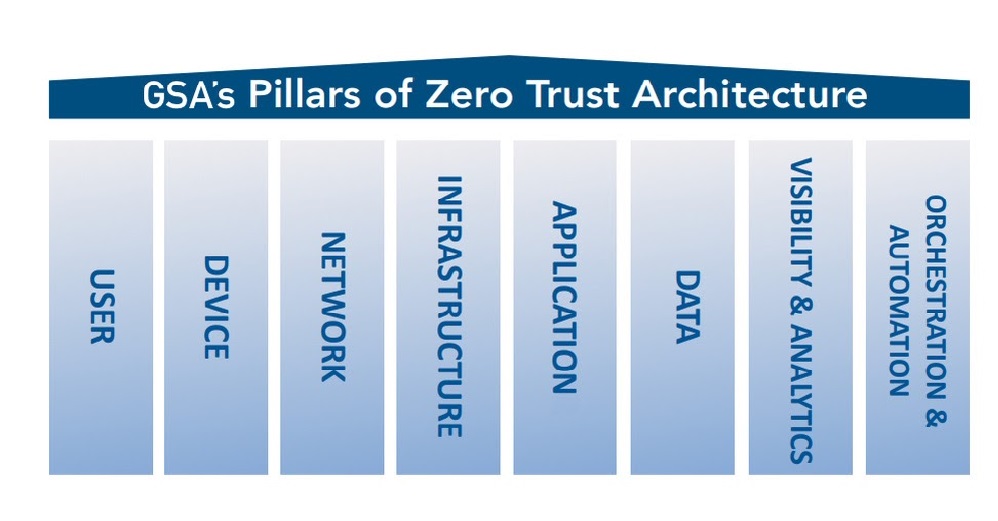
May 2022 marked one year since President Biden signed Executive Order (EO) 14028 – “Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity.” It directs sweeping changes to cybersecurity requirements and calls on federal agencies to address key issues critical to building a more resilient cybersecurity posture. The EO also requires federal agencies to take steps to implement a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) model to modernize and strengthen cybersecurity standards and detection.
Since May 12, 2021, the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) issued additional guidance to support the mission of “Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity.”
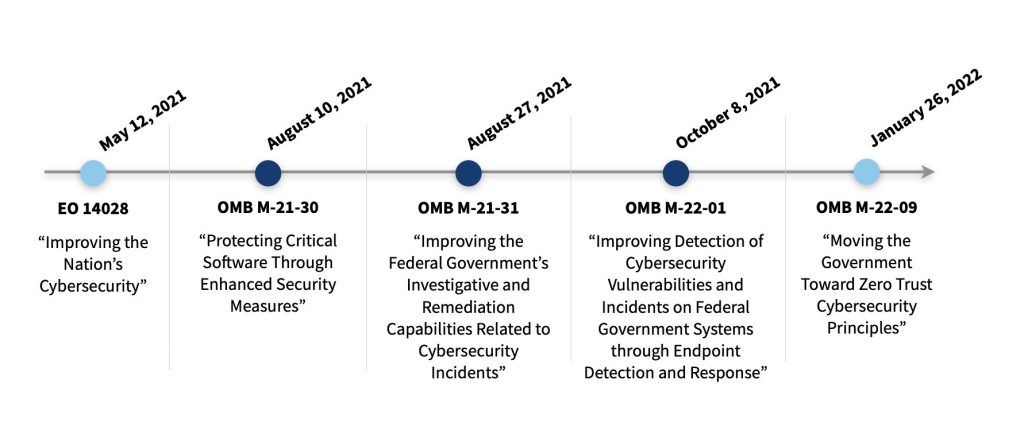
The associated OMB memos outline the steps required for agencies to better protect federal information systems, making them more secure and resilient. The requirements include implementation of:
- Strict security controls on critical software,
- Mature event detection and analysis capabilities, and
- Endpoint data collection within networks to detect and hunt cyber threats.
Federal agencies also have new ways to obtain funding for the cybersecurity products and services needed to implement the EO’s requirements. Bolstering cybersecurity defenses is one of the Technology Modernization Fund (TMF)’s focus areas, and it’s funded three projects to support ZTA implementation. The President’s FY23 Budget request includes increased funding for federal agencies as they implement the EO’s priorities and a ZTA strategy. The request is the largest such increase in over 12 years.
Resources to help meet the EO requirements
There is no single technology, product, or service that can achieve the goals of implementing ZTA. Each agency’s journey and solution will be unique, and GSA’s Federal Acquisition Service (FAS) is here to help.
The FAS Office of IT Category (ITC) has resources to help agencies, vendors, and acquisition professionals continue to work towards a mature ZTA and meet the Administration’s requirements.
Over the past year, GSA’s ITC has:
- Participated in governmentwide working groups on Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) and ZTA. To ensure GSA’s offerings are capable of delivering the products and services that support implementation of the EO’s requirements, subject matter experts (SMEs) participated in working groups led by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
- Educated the acquisition workforce on EO 14028. GSA SMEs conducted multiple trainings and speaking engagements for IT and acquisition professionals on ZTA, C-SCRM, and the EO requirements. If your agency would like to schedule a session with GSA SMEs, reach out to the GSA National Account Manager dedicated to your agency.
- Incorporated C-SCRM practices into GSA contract vehicles. To assist agencies with EO requirements to mitigate cyber risks in the Government’s IT supply chain, GSA continues to pursue efforts to ensure alignment with EO guidance.
- Developed informational webpages and Buyer’s Guides to aid agencies navigating the EO requirements.
Other ways GSA can help
Whether your agency is small or large, GSA has solutions that can be tailored to your cybersecurity needs. In addition to the Buyer’s Guides, GSA offers multiple online tools to assist in planning a cybersecurity acquisition.
- IT Security Acquisition Planning Package (APP) provides common resources agencies can use to plan a cybersecurity acquisition, including:
- Overviews of GSA IT Security offerings,
- IT Security Statement of Work (SOW) and Request for Quote (RFQ) templates, and
- GSA’s Market Research As a Service (MRAS) tool to identify potential vendor pools and suggested contract vehicles.
- GSA developed Buy.GSA.gov, which can help you:
- Plan – Determine the documents you need, and find vendors and contracts.
- Develop Documents – Find sample documents and templates.
- Research – Find products, services, and pricing data.
- Purchase – Review buying methods and request submissions for quotations.
- GSA, in partnership with the Federal Chief Information Officers Council, is developing a series of ZTA Playbooks to help agencies move from the conceptual planning phase to actual implementation of a zero trust security model. Agencies can expect a “base playbook,” followed by playbooks dedicated to the pillars of a mature ZTA.
- GSA has Customer Service Directors specifically assigned to your agency by location. You can also find the National Account Manager dedicated to your agency.
- For cybersecurity SME support, contact the IT Security Subcategory at ITSecurityCM@gsa.gov.
What’s next
As the Federal government improves its efforts to better protect Federal information systems, expect additional OMB guidance and updates to the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR), driving the need for modification of contract language. GSA will keep you informed, communicating with you the major developments.
Follow ITC on Twitter and LinkedIn, and subscribe for blog updates.